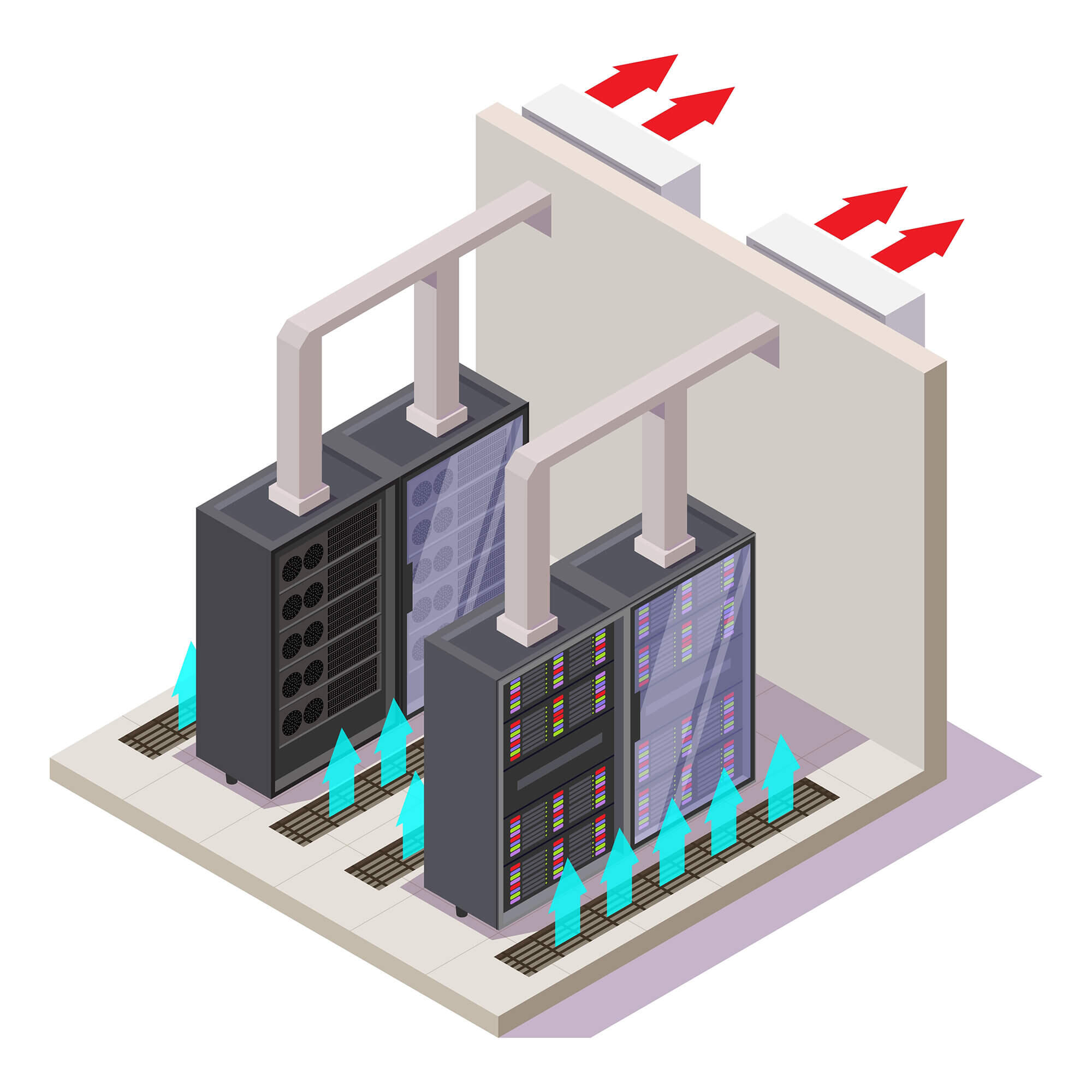
THE PRODUCT:
Computer room air conditioners (CRACs) are similar to other air conditioning equipment but are intended to cool places such as computer rooms, server rooms, and data centers. CRACs are often referred to as “precision cooling” equipment. While most air conditioners are designed to remove both heat and humidity, CRACs are designed to primarily lower the temperature of the room (i.e. they have high sensible heat ratios). Some computer rooms and data centers utilize separate equipment for controlling humidity. CRACs can be air-cooled, water-cooled, or glycol-cooled.
CRACs are a category of ASHRAE equipment.
THE STANDARD:
The current standards for CRACs took effect in 2024. The efficiency levels are equivalent to the efficiency levels in the 2019 version of ASHRAE 90.1, expressed in the cooling energy efficiency metric net sensible coefficient of performance (NSenCOP).
*The cooling energy efficiency metric, NSenCOP, is expressed as the net sensible cooling capacity (kW) divided by the power input (kW).
KEY FACTS:
Technology options for improving the efficiency of CRACs include higher-efficiency compressors, fan motors, and expansion valves and improved heat exchangers.
Timeline
| Federal | Date |
| Next Review Due | 2029 |
| 2nd Federal Standard Effective | 2026 |
| 2nd Federal Standard Adopted | 2023 |
| 1st Federal Standard Effective | 2013 |
| 1st Federal Standard Adopted | 2012 |